Digital Forensics: An Introduction
Digital
Forensics is the application of scientific methods in preserving, recovering,
and investigating digital evidence in a Digital crime scenario. It can be correctly defined as, collection,
examination, analysis, and documentation by using scientifically proven methods
to investigate a digital crime and present it before the court.
Table of
Contents:
Ø Elements
of a Digital Crime
Ø Goals
of Digital Forensic Investigation
Ø Classification
of Digital Forensics
Ø Digital
Evidence
Ø Principles
of Digital Forensics
Ø Process
of Forensic Investigation
Ø Types
of Tools
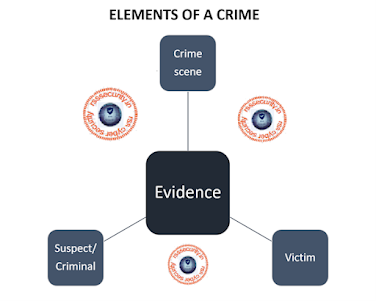
Ø Elements of a Digital Crime
To prove a digital crime, as an investigator you should have the
following elements to bring out a conclusion. All the elements will be related
to one another in a more or so.
Ø Goals of Digital Forensic Investigation
As a digital forensic investigator, you should have a goal for
investigation. Depicted below are the five most important goals of investigation;
Classification of Digital Forensics : Digital forensics is a very broad term that has various classifications within it. The most popular forensic investigations are as follow:
Computer Forensics: It is the most primitive type of digital forensics which usually was introduced in the early evolution of computer systems. It includes investigating computers, laptops, logs, USB drives, hard drives, Operating systems, etc.
Network Forensics: It includes investigating by analyzing network events, intrusion, and data packets that were transmitted to detect network attacks.
Multimedia Forensics: It comprises of investigation of images, audio, and video files that are recovered as evidence in a digital crime scene.
Mobile Forensics: It comprises of investigation of Smartphone’s like android, iOS, etc for finding digital evidence and recovering the deleted data important for the case.
Memory
Forensics: It is the forensic investigation of the memory or ram dump of the
system to find out volatile memory like chat history, clipboard history,
browser history, etc.
Cloud Forensics: Considering the virtual storage are in demand, the investigation of the cloud environment also plays a key role in a digital crime scene for gathering evidence.
The classification of digital forensics isn’t limited to the above diagram and as t can be classified into more depending on the cases.
Ø Digital Evidence
Digital
evidence or electronic evidence can be defined as any object that stores
digital information and transmits it in any form which was used in the act of
crime or in supporting the investigation of the case in a trial before the
court.
The
evidence found at the crime scene should have two key properties
.They
should be admissible in the court.
.They
should be authentic.
The
digital evidence can be like of various types and should be availed ethically
by following the prescribed guidelines of investigations. Here are a few
digital evidences in the diagram below, but the list goes on.
Understanding Data and Metadata:
The difference between the data
and the metadata for the forensic investigation can be easily understood with
the help of the diagram below;
Principles of Digital Forensics:
1) Securing the Crime Scene: This is the most primary principle of Digital Forensics. As an investigator you should prohibit any access to your suspected digital evidence, document all processes and connections, disconnecting wireless connections, etc. to keep your evidence secure.
2) Limiting evidence
Interaction: As an investigator, you should make
sure that your evidence is having a limited interaction by capturing the ram
and can also perform cold boot attacks on the evidence.
3) Maintaining Chain of
Custody: Chain of custody is a record of sequence
in which the evidence was collected, date and timestamps at the collection, the
investigator who accessed and handled it, etc.
Process of Digital Forensic Investigation
Identification: This is the first step that an
investigator takes at the crime scene is to identify the purpose of the investigation
and recognize the potential digital evidence.
Preservation: This is the next step where the investigator has to be careful as he should make sure that the evidence has not tampered which may complicate the investigation.
Collection: This step involves acquiring the evidence most appropriately without causing any harm to the evidence and packing it in a Faraday Bag.
Examination: This step is a precursor to performing any analysis of the evidence. This step requires careful inspection of the evidence for any other secondary details.
Analysis: In this step, the investigator carries out the most crucial things like joining the bits and pieces of the pieces of evidence, retrieving deleted files, etc.
Interpretation: This step involves concluding the investigation finding after reconstruction of the crime scene.
Documentation: This step usually involves preparing a detailed report or a document on the entire investigation.
Presentation: This is a mandatory step only when it is asked for cross-examination which is to be mentioned in very simple terms of understanding for commoners.
Types of Tools:
An investigator needs to have the right set of tools for conducting a digital forensic investigation. It is for the investigator to decide the tool appropriate for the case. The tools also depend on the application based on hardware and software. The types of tools can be classified into three types; Open Source, Proprietary, and Self created.
Tool name – OSForensics [ https://www.osforensics.com/ ]
Conclusion: Hence, we have covered the basic understanding and requirements for Digital Forensic Investigation.








.png)






0 Comments
Refer to a specific part of their comment that you appreciate. Relate to them if you can.